A process called apomixis In one form, the egg is formed with 2n chromosomes and develops without ever being fertilized; Updated Spores are reproductive cells in plants;In asexual reproduction in plants, plants are reproduced without the formation of seeds Following are a few ways in which plants reproduce asexually Vegetative Propagation As the name suggests, reproduction occurs through the vegetative parts of a plant such as stems, leaves, buds, and roots

Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
How seeds reproduce
How seeds reproduce- The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants This is one of the ways that plants like liverworts and mosses reproduceAlgae and other protists;




Fruit And Seed Dispersal Biology For Majors Ii
Vascular plants can be divided into two main types seedless and seedbearing Seedless plants are those which do not reproduce by producing seeds like seedbearing plants Rather, they produce a larger number of small, singlecelled spores Most of the trees one might encounter in a contemporary forest today would be seedbearing, vascular plants "Plants have different ways of reproducing young plants Plants can reproduce by seeds, spores; Seed dispersal allows plants to spread out from a wide area and avoid competing with one another for the same resources Seeds are dispersed in several different ways In some plants seeds are
Through being carried away in rivers or the sea to somewhere the seeds can germinate What is the best time to collect fruits and seeds for the tree nursery?And fungi They are typically singlecelled and have the ability to develop into a new organism Unlike gametes in sexual reproduction, spores do not need to fuse in order for reproduction to take place Organisms use spores as a means of asexual reproductionThey reproduce by creating spores Unit 1 Plants 3 mold nutrition plant seed stem moho alimento planta semilla tallo
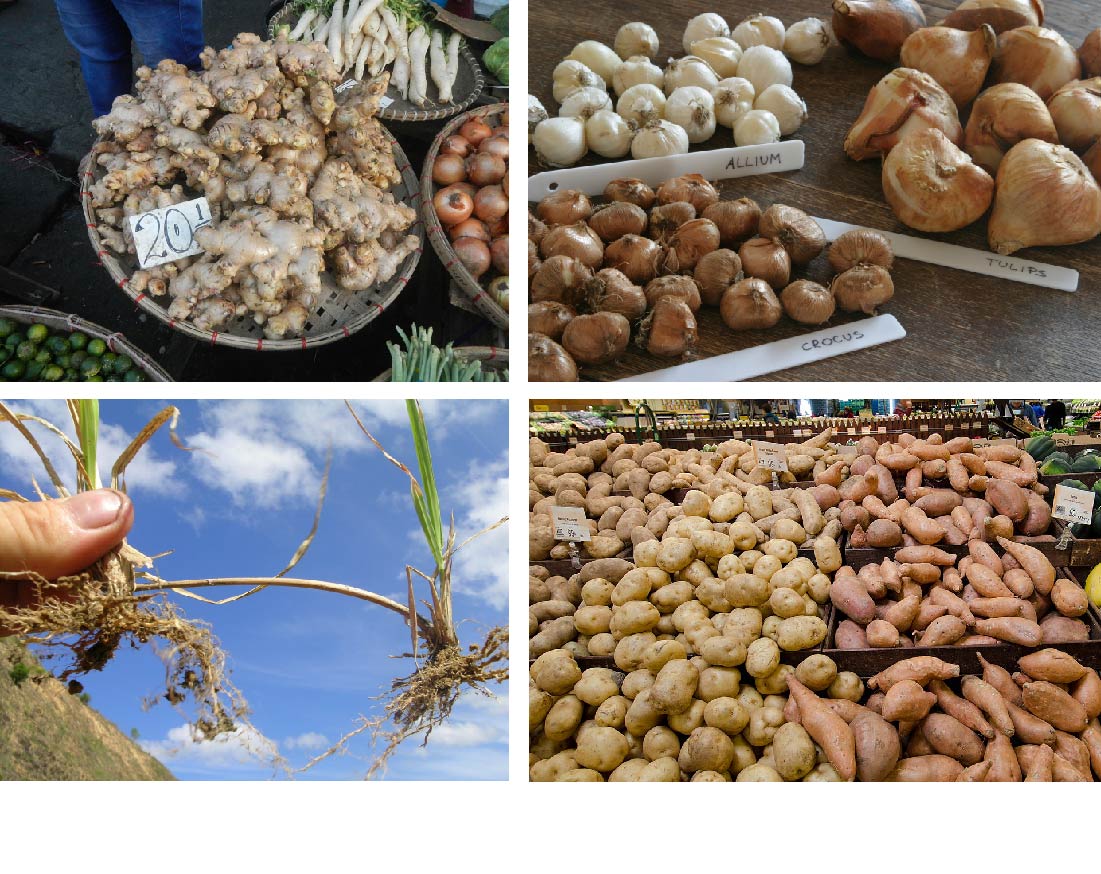
The seed has an embryo protected with a hard coating The ovary with time grows into a fruit with the seed still inside They are embryonic and often contain protein The dispersion of seeds is by water, air, animals, and other agents as well Some pollinators are often animals, especially spiny seed plants Urena and Xanthium are examples of thisStem cuttings, leaves, underground stems and runners Usually it has been observed that some flowering plants such as balsam, tomato, papaya and a few other are reproduced by seeds Plants which reproduce by underground stems are potato, ginger, onionThe video explains how plants reproduce without a seed like potato plant reproduce from stem, strawberry reproduce from runner, few plants can reproduce from




List Of Asexually Reproducing Organisms




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download
Reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual Asexual reproduction In asexual reproduction new plants are obtained without production of seeds Vegetative propagation It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds Since reproduction is through theAmong liverworts, mosses, lycopods, ferns, and seed plants, fewto manycelled specially organized buds, or gemmae, also serve as agents of asexual reproduction The vegetative, or somatic, organs of plants may, in their entirety, be modified to serve as organs of reproductionTheir own source of energy For example, molds are parasites obtaining their energy directly from the plant or animal they live on — their host Furthermore, plants such as molds do not reproduce through seeds;




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow



Dk Science Seed Plants
Plants That Reproduce From Suckers Some plants reproduce from suckers, which sprout from the plant's lateral roots These suckers create newFor example, winged seeds of drumsticks, hairy fruit of sunflower, etc are dispersed by wind (c)Dispersal by water – Many aquatic plants or plants that live near water has seeds that can float and are carried away by water For example, coconuts can float and are dispersed by waterThrough being taken and buried by certain animals;




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications




Plant Asexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube
Examples of plants propagated at the hardwood stage include forsythia, privet, fig, grape, and spirea The three types of hardwood cuttings are straight, mallet, and heel (Figure 3) A straight cutting is the most commonly used stem cutting Mallet and heel cuttings are used for plants that might otherwise be more difficult to root Plants reproduce asexually from roots and stems, from cell tissue that grows from leaves and stalks, and from seeds that grow without fertilization taking place Examples of asexual plant reproduction are commonplacePlant reproduction is the process by which plants generate new individuals, or offspring Dry fruits are usually adapted for wind dispersal of seeds, as for example with the assistance of winglike structures or a fluffy pappus that provides buoyancy The diversity of fruiting bodies reflects in part the diversity of dispersal agents in the




Planting Bulbils What Are Bulbils And How To Grow Plants From Bulbils




Seed Wikipedia
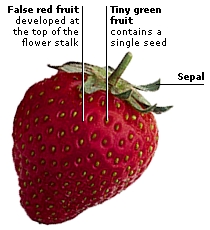
Strawberry plants can reproduce through sexual reproduction with fruit and seed, as well as through asexual reproduction by sending out runners to create new plants, according to Garden Guides Runners, also called stolons, are sent out from the crown of a strawberry plant along the ground Nodes begin to appear on each stolon at set intervalsReproduction is an essential characteristic of all living organisms • eg mango and coconut Pome • juicy part is swollen receptacle • is usually a false fruit • example is a pear membrane inside the testa Hilum • a scar • spot where the seed was attached to the fruit or pod Micropyle • small hole through which water andPlant reproduction without seeds is present in mosses and ferns These plants combine sexual and asexual reproduction When the female and male gamete meet, structures are formed called spores These spores, once they are developed and mature, are then impulsed by wind until they fall on the floor and germinate, then new plants are born




Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Welcome To Miss Ng Science S World Life Processes Of Plants
Sporophyte Definition Plants may look simple, but the way they preserve their species is anything but They have a life cycle which involves alternation between a generation of one set of chromosomes and two sets of chromosomes in order to reproduceWhile the term sporophyte is referred to as plants that produce spores, the real definition is more complicatedAll plants can reproduce through seeds, except for those hybrids/cultivars that are so radically modified that they have lost reproductive function Seedless watermelon and hybrid tea roses would be examples of those that CANNOT reproduce form seed 490 viewsTrees reproduce sexually through seeds (female) and pollen (male) Gymnosperms produce a naked seed whereas angiosperms (flowering plants) produce a true seed



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora




Biology Reproduction Notes
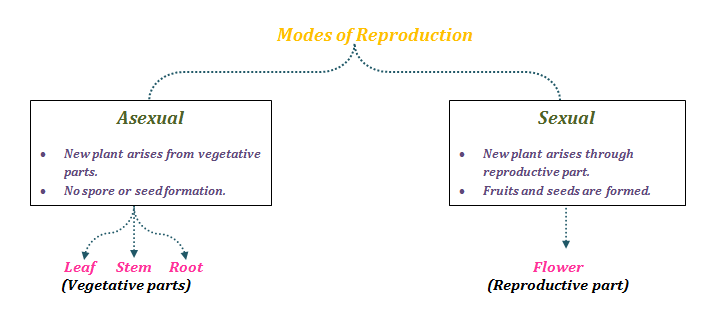
Agamospermy, asexual reproduction through seeds, occurs in flowering plants through many different mechanisms and a simple hierarchical classification of the different types is not possible Consequently, there are almost as many different usages of terminology for apomixis in angiosperms as there are authors on the subject Apomixis Citrus trees and many other species of angiosperms use their seeds as a method of asexual reproduction;Asexual reproduction does not involve the production and fusion of male and female gametes Asexual reproduction may occur through binary Fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, regeneration and vegetative propagationPlants have two main types of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced that are genetically identical clones of the parent individual




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia




Fruit And Seed Dispersal Biology For Majors Ii
Some examples of vegetative propagation are farmers creating repeated crops of apples, corn, mangoes or avocados through asexual plant reproduction rather than planting seeds Vegetative propagation can be accomplished from sideshoots, slips, stems and sections of tubers, bulbs or rhizomesThe establishment of clonal seed orchards The establishment of clonal banks The propagation of special breeding material, eg exceptional hybrids that are lost through sexual reproduction, sterile hybrids etc Mass propagation of selected materials There areSeed 1 Part of the sexual reproduction of angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (cone plants) Contains an embryo and its food store, which creates a new plant when conditions are right 2 Offspring or progeny spores Small reproductive structures that can grow into a new individual



Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia
Keep a close watch on the parent trees (B 21–22) which you have chosen for collection Vegetative Propagation is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds Since reproduction is through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation Bryophyllum (sprout leaf plant) has buds in the margins of leavesDK Science Seed Plants Most plants grow from seeds These seed plants fall into two groups, angiosperms and gymnosperms Angiosperms are the flowering plants Their seeds develop inside a female reproductive part of the flower, called the ovary, which usually ripens into a protective FRUIT Gymnosperms (conifers, Ginkgo, and cycads) do not



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub
Seeds A seed vascular plant produces female megaspores, or seeds, that the plant retains through maturity In a gymnospermmeaning "naked seed"the ripe female seed separates from the plant andRoots such as corms, stem tubers, rhizomes, and stolon undergo vegetative reproduction Some plants can produce seeds without fertilization via apomixis where the ovule or ovary gives rise to new seeds Advantages of asexual reproduction include an increased rate of maturity and aIrises can reproduce sexually through pollen and seeds but sometimes will use rhizomes to reproduce as well This is why you may see a patch of irises growing close together



How Does Onion Reproduce Its Stems Leaves Or Roots Quora




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
The Great Plant Escape is an elemertary plant science program for 4th and 5th grade students Each of the lessons in this program is interdisciplinary, designed to introduce students to plant science and increase their understanding of how food growsSeed plants reproduce by means of seeds Examples of seed plants are numerous, and include soybeans, oranges, raspberries, broccoli, prunes, corn, peaches, mangoes, celery, conifers, tangerines, kiwifruit, gooseberries, plums, pumpkins, beets, starfruit, all types of beans, carrots, asparagus, apples, crabapples, swiss chard and more Vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction is the growth and development of a plant by asexual means This development occurs through the fragmentation and regeneration of specialized vegetative plant parts Many plants that reproduce asexually are also capable of sexual propagation




Group 1 Plants That Make Seeds




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia
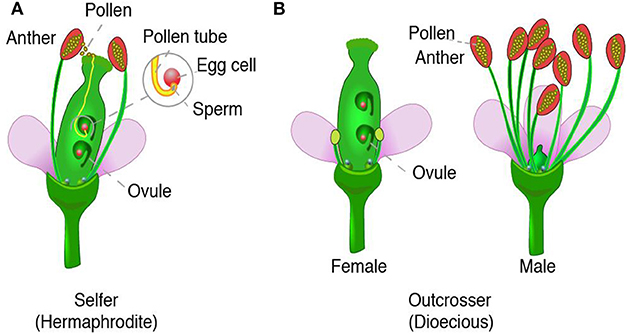
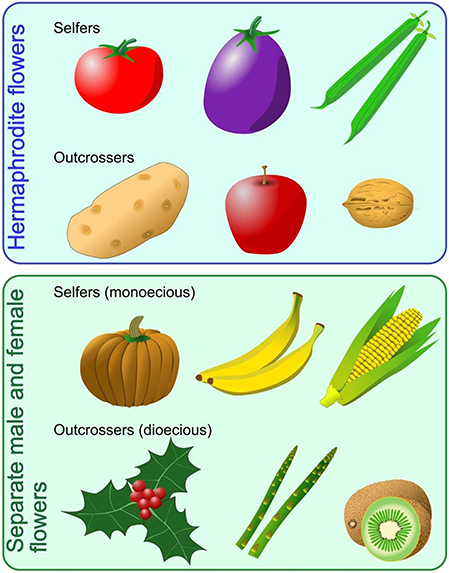
A twocelled microgametophyte (called a pollen grain) germinates into a pollen tube and through division produces the haploid sperm An eightcelled megagametophyte (called the embryo sac) produces the egg Fertilization occurs with the fusion of a sperm with an egg to produce a zygote, which eventually develops into an embryoGymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms include Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants This type of reproduction occurs when new individuals are formed without the production of seeds or spores The formation of new plants out of rhizomes or stolons is an example of vegetative reproductive, such as in the strawberry plant




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed Through Spores Vegetative Reproduction Hindi Youtube
In sexual reproduction, a fusion of male and female gametes produces fruits that contain seeds The seeds give rise to new plants A flower is the reproductive part of a plant which can either be unisexual or bisexual Stamen is the male reproductive part and pistil is the female reproductive part of a flowerIn another version, the cells of the ovule (2n) develop into an embryo instead of or in addition to the fertilized egg




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube




4 Main Types Of Plants For Kids




How Plants Are Classified Part 2 Reproduction Ppt Download




Seed Bearing Plants Science Learning Hub




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




4 02 Methods Of Plant Propagation Sexually And Asexually Propagating Plants Ppt Download




Hypogeal Germination Vegetative Propagation Stages Examples Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Plant Reproduction Bioninja
/cycad_cones-5ae333e9a9d4f9003736fc5e.jpg)



Gymnosperms Definition Examples And Reproduction




Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Plant Reproductive System Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica
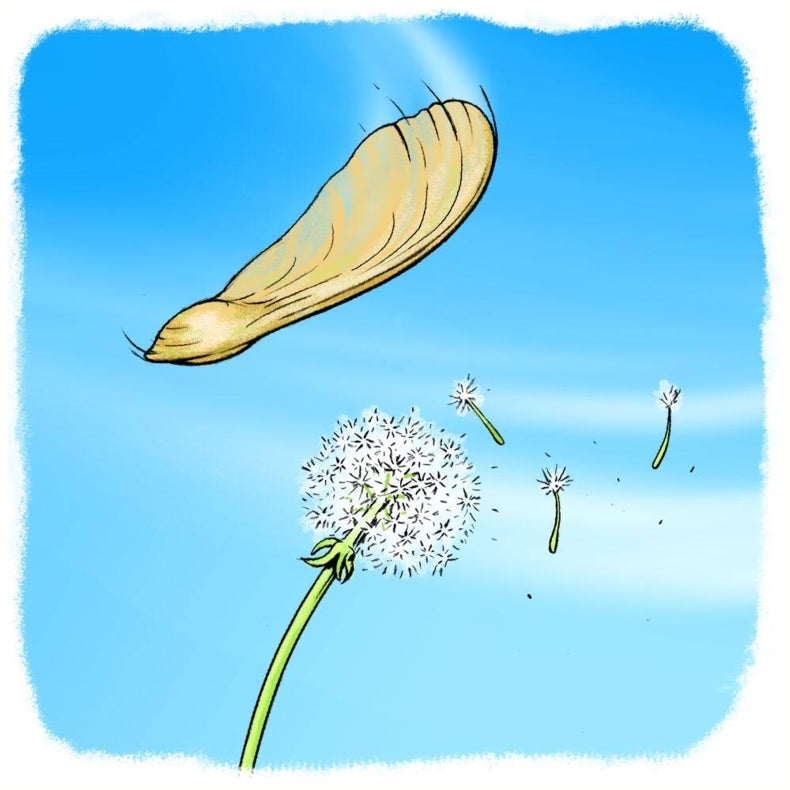




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American




Flowers Ppt Download




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds
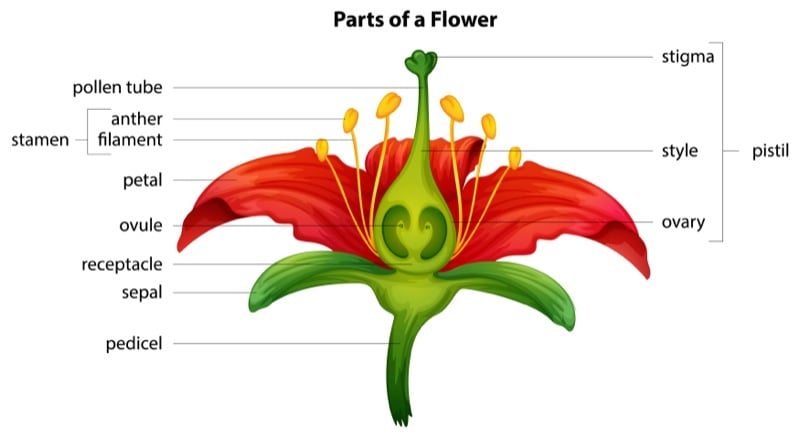



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Nonflowering Plants Lesson For Kids Names Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



1




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Plant Reproduce




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
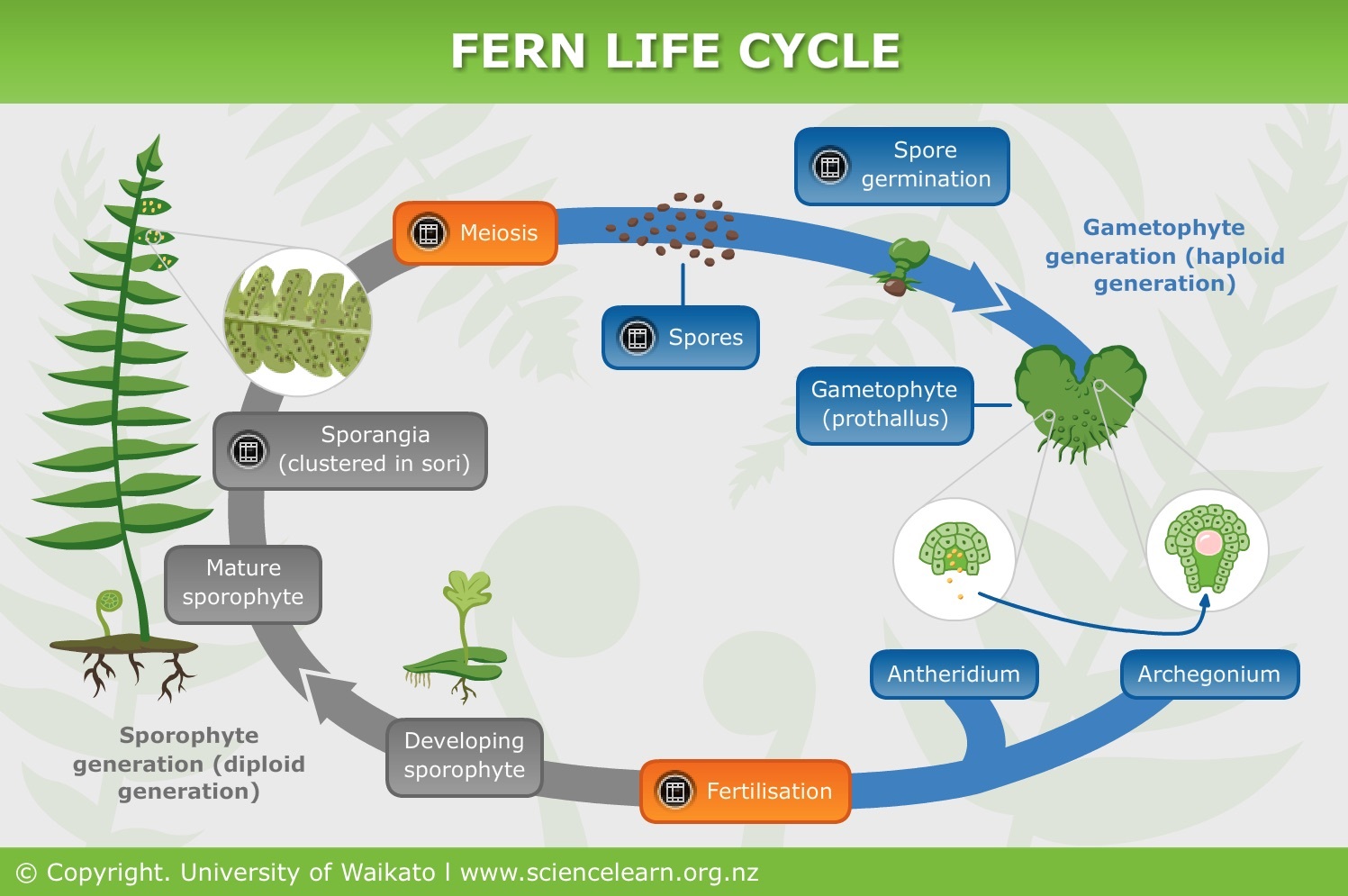



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Flowering Plant Life Cycles Science Learning Hub




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Pin On Science




Seed Dispersal Reproduction In Plants Don T Memorise Youtube




Sexual Reproduction In Animals And Plants Comparison And Examples




Angiosperm Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Dk Science Seed Plants



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Plant Reproduce




The Difference Between Seedling Grafted And Cutting Grown Fruit Trees Deep Green Permaculture
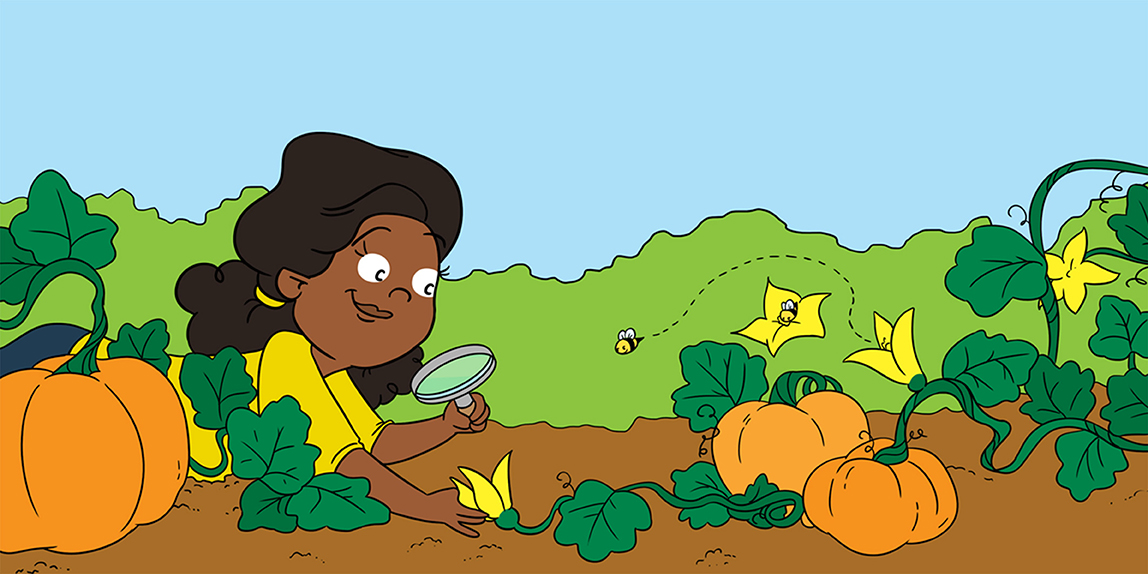




Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Sexual Reproduction In Plants Plants Biology Fuseschool Youtube
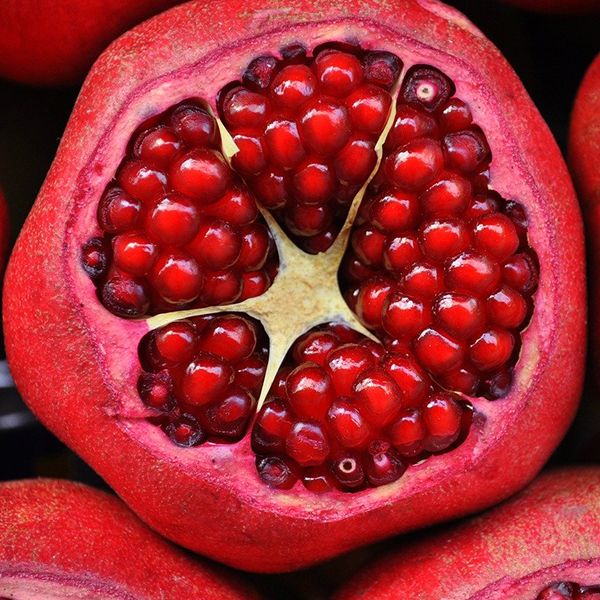




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Plant Classification Project Ppt Download




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Seed Dispersal Methods Benefits Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Plant Reproduction 6 2 3 6 2 4 Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download
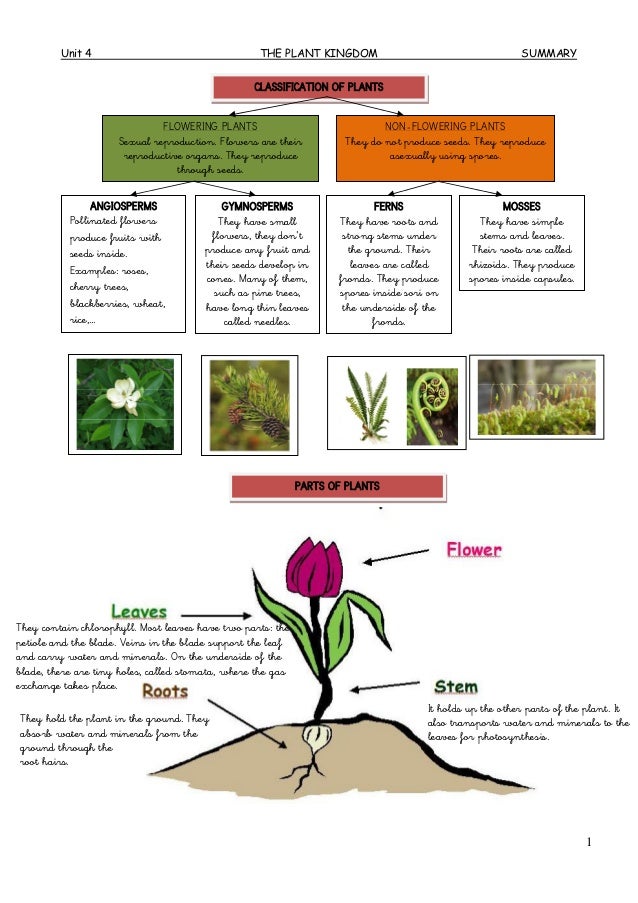



Unit 4 Diagram



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Plants Test
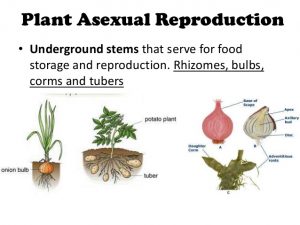



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online



Plants Which Reproduce Through Leaves
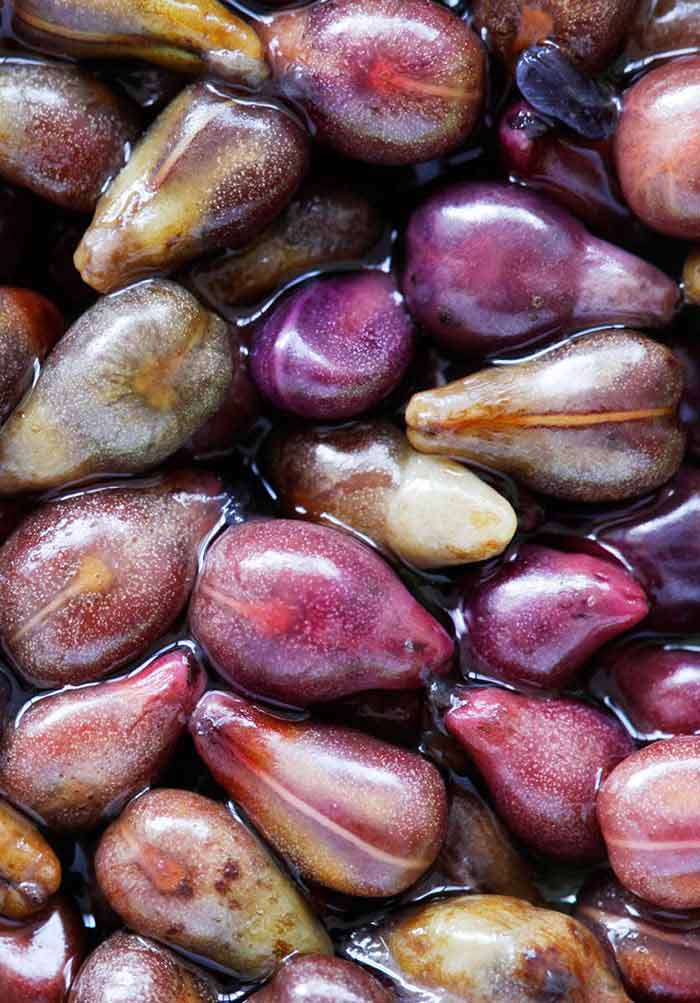




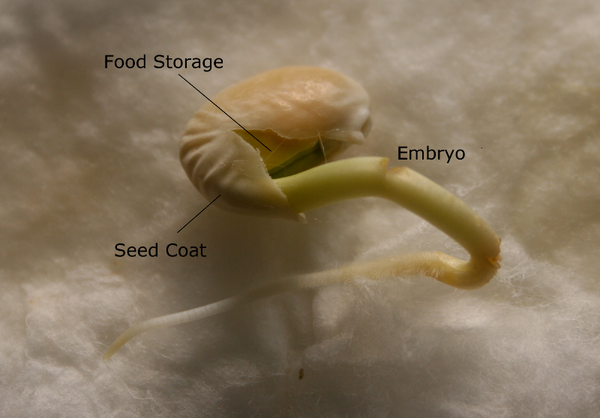
Metabolic Processes During Seed Germination Intechopen
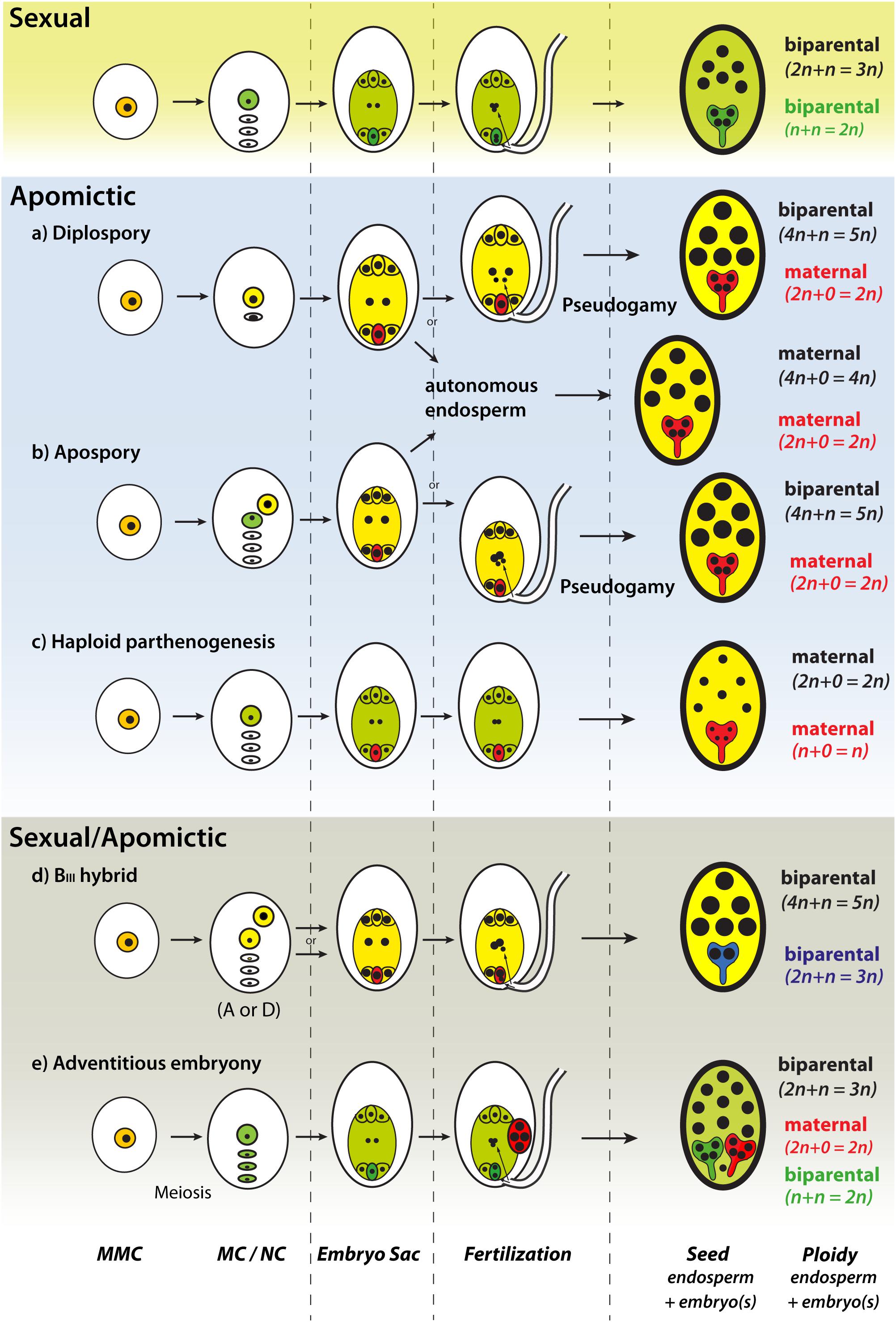



Frontiers The Rise Of Apomixis In Natural Plant Populations Plant Science




What Are Some Examples Of Flowering Plants That Do Not Reproduce From Seeds Quora



1




Sexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-826588476-5a7b42c6c064710037c3ef73.jpg)



Fern Reproduction And Life Cycle




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
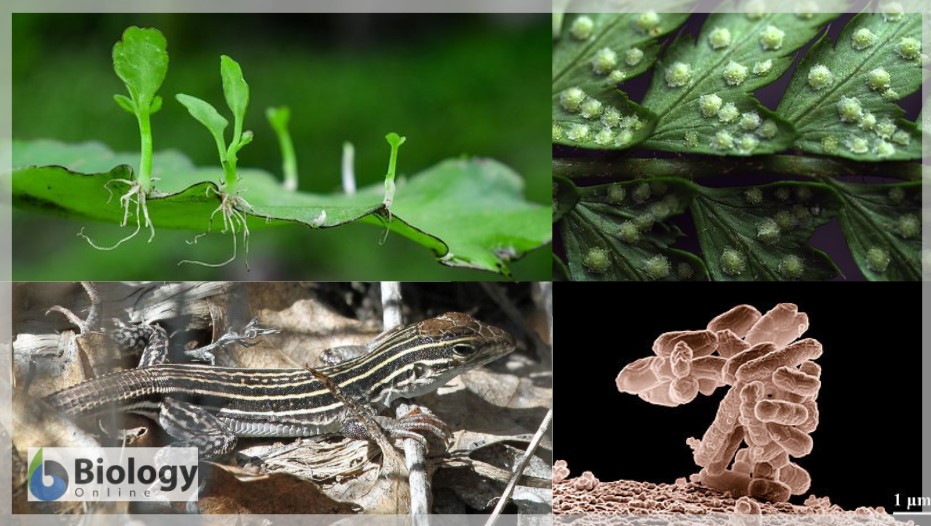




Asexual Reproduction Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Kingdom Plantae Study Guide
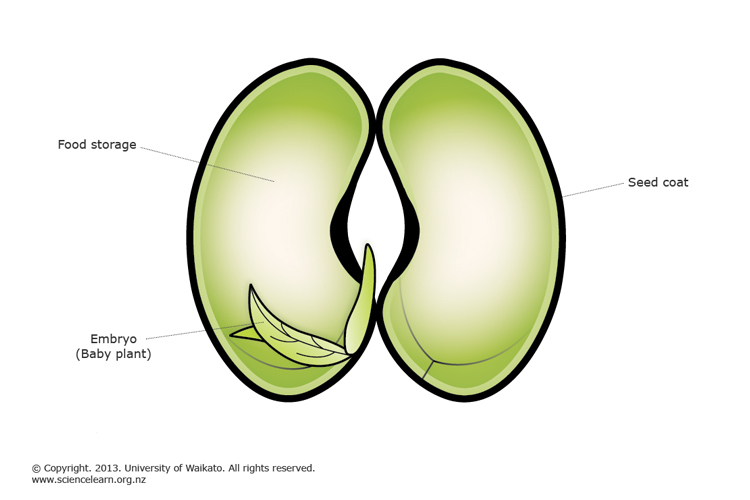



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




23 Easiest Vegetables To Grow From Seed Get Busy Gardening



Q Tbn And9gcqy9wuzklahycc9 Ktqoconahtwyb6c2a37il9scvsrouasu38t Usqp Cau




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Asexual Reproduction Boundless Biology




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




4 Main Types Of Plants For Kids




Plant Reproductive System Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica
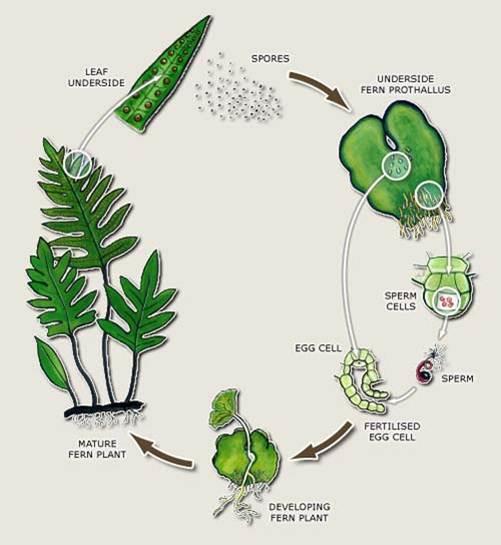



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express
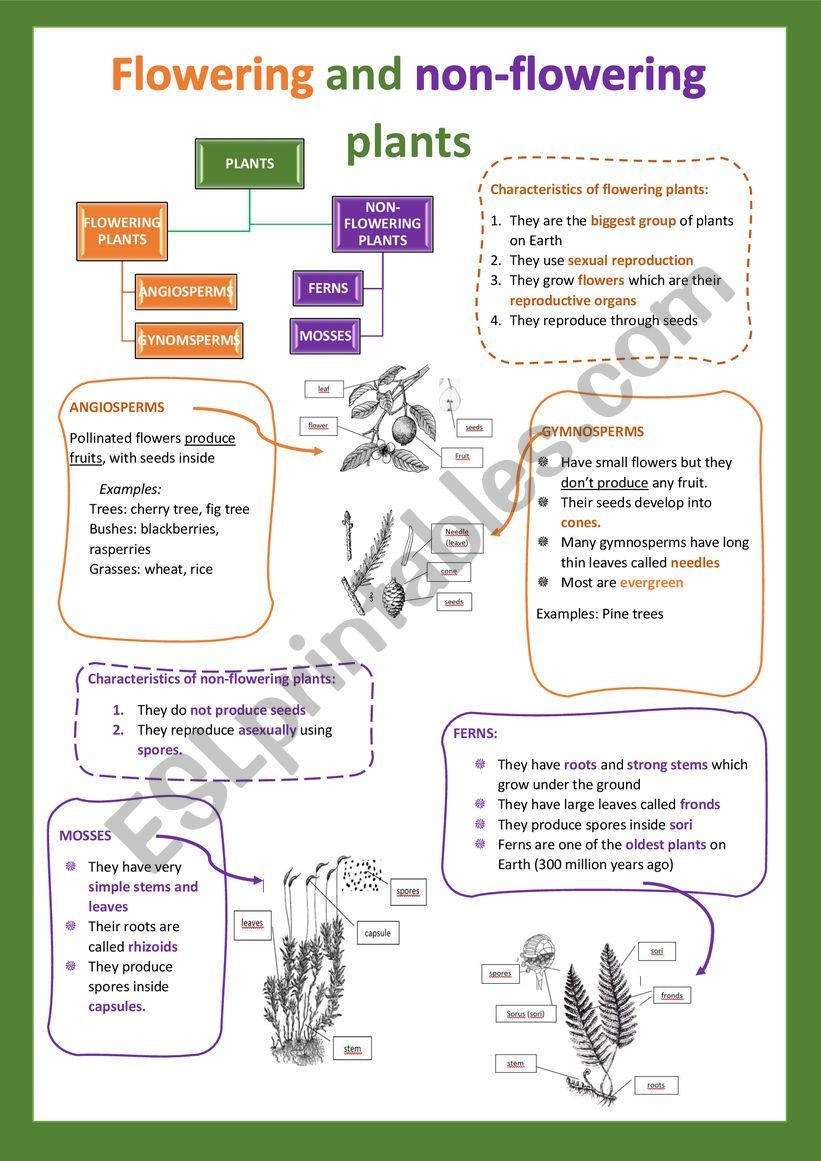



Flowering And Non Flowering Plants I Esl Worksheet By Cristinasuma




1 Seeds Of Some Plants Don T Germinate How Are Their Next Scholr



1




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




8 Plants That Grow From Leaves Plants That Reproduce From Leaves




The 10 Easiest Plants To Grow From Seed Finegardening




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
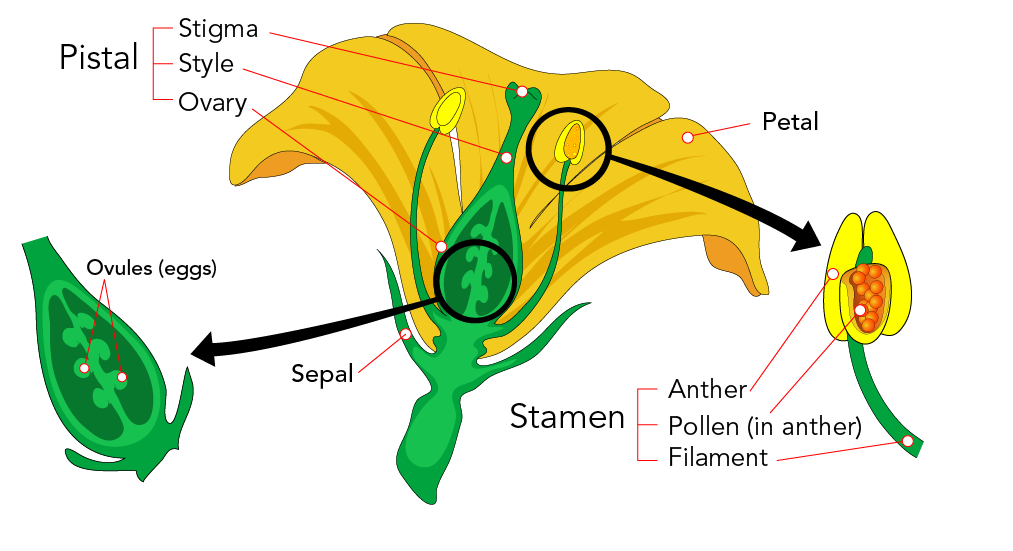



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial




Angiosperm Seeds Britannica




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿